A Cloud Development Environment (CDE) is implemented with a container or virtual machine accessible for the purpose of supporting code development activities. Here is a brief history of this technology, how it was recently recognized as a Gartner category, and a summary of the benefits of coding online.
A brief history of cloud-based development
The aim of Cloud Development Environments is to enable software development to move online. This approach to coding online has an interesting history that dates back to the mid-2010s when a handful of innovative startups took their first steps into this emerging field.
As time went on, several of these early ventures were acquired by larger tech companies, who saw the promise in their innovative ideas. So, when we talk about CDEs today, we are actually looking at a concept that had its roots in the forward-thinking landscape of the mid-2010s.
Grasping the concept of a Cloud Development Environment
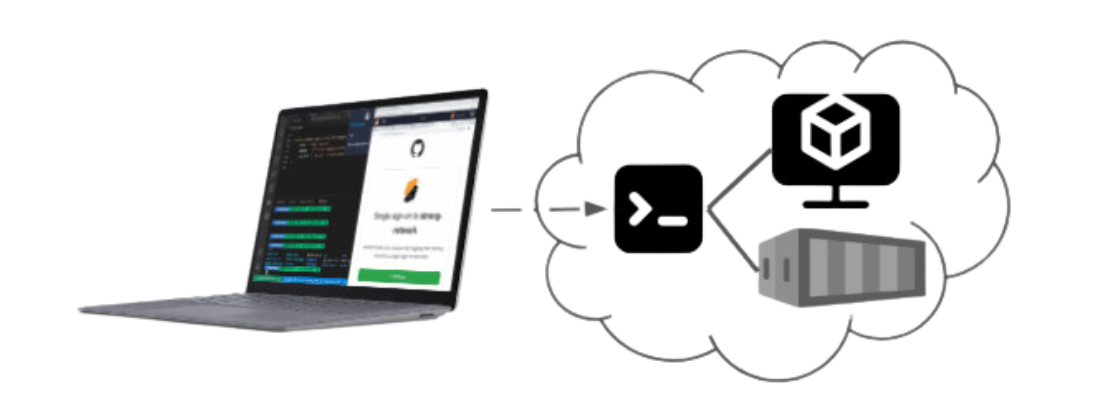
Fast-forward to 2023, industry analyst Gartner suggests calling the technology a Cloud Development Environment. A CDE is like connecting to a remote machine through a terminal command window, such as using an SSH client. Such a remote machine can be a physical host or a virtual process like a container or virtual machine.
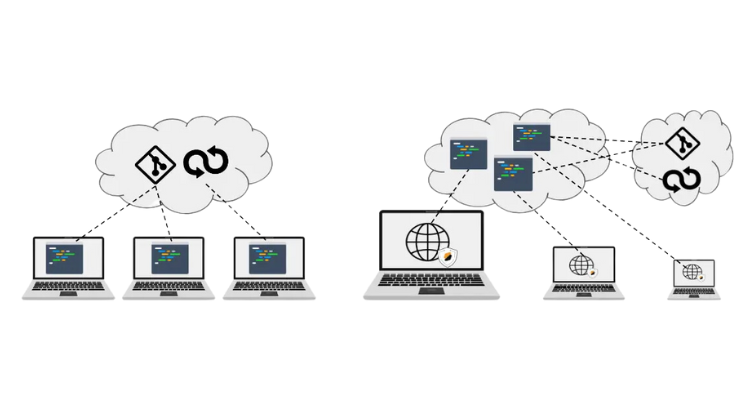
For the sake of efficiency, running CDEs online might typically rely on technologies such as lightweight virtualization, e.g. Docker or Podman, but virtual machines are also viable candidates albeit slower.
The typical specification of a CDE is typically a Linux OS with a series of applications and packages, with the goal to provide a ready-to-use, fully-configured development environment. Embed an IDE as a web application and you have all the components to start writing code online.
Using a web-based IDE (try Microsoft Visual Studio Code) a typical onboarding on the CDE goes like that: the developer opens a URL that loads the IDE into the browser and, in addition, gets a terminal prompt to the online CDE.
What are the benefits of CDEs for developers and organizations?
Managing developments online has a benefit. Organizations can offer a self-service option for developers. This allows them to access pre-set environments without IT help. These environments include approved software, packages, and computing capabilities provided by the CDE.
This method works for any developer, but self-service is best for internal employees. In contrast, a managed access to environments is also possible for contractors or temporary employees.
Improved governance and security for development using CDEs
CDEs can be managed, updated, and improved online without needing the developer’s computer. They can be checked in real time, like monitoring a process in the cloud, to see productivity and security metrics. In addition, the online nature of cloud development environments make them extremely attractive to onboard developers regardless of their location.
Lastly, there is an opportunity to handle security better from the standpoint of resource access control, network monitoring and data loss prevention.
How CDEs automate DevOps and DevSecOps workflows
Bringing development environments online strongly benefits interactions with commonly used DevOps tools and applications. Most importantly, the use of CDEs cannot hinder any existing tools. Communication is easier because CDEs, DevOps, and DevSecOps tools are all available online. This makes automation easy.
In conclusion, CDE technology is driving the fastest DevOps transformation trend today with the entire cloud-native development industry moving development environments online.
An extended version of this article is available on DZone, the best place for community exchanges around DevOps.