
Application security, sometimes referred to as app security or AppSec, is a collection of security measures applied at the app level to prevent data or code from being misused, stolen, or harmed. It’s a comprehensive approach used to address security issues during application development, design, and deployment—and to prevent security vulnerabilities that may lead to an attack.
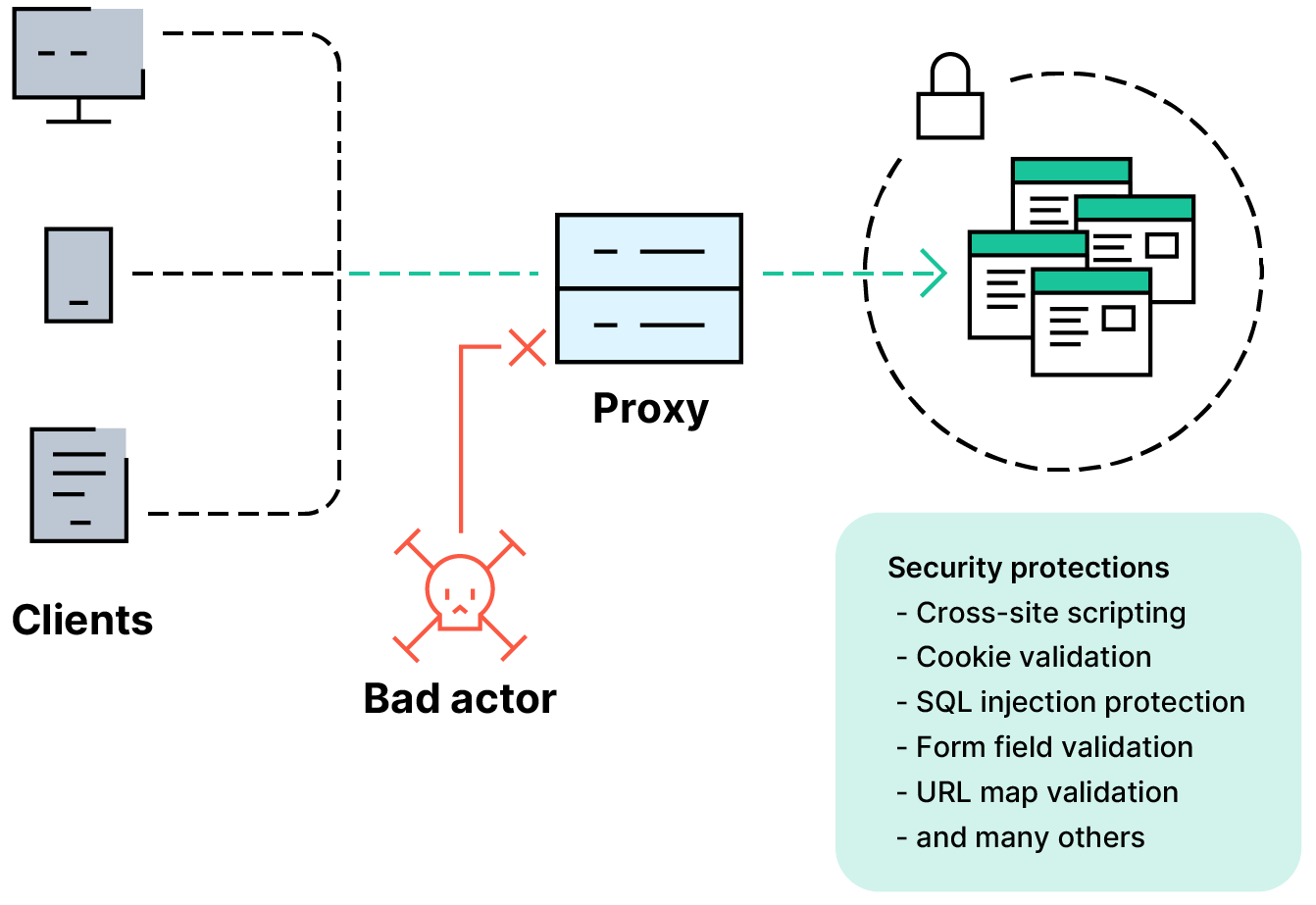
Application security solutions often include a mix of security software and hardware devices to minimize risks and vulnerabilities. Application security solutions often include application delivery controllers (ADC), integrated web application firewalls (WAF), encrypted routers, and other application delivery tools.
The solution
Who needs to implement application security solutions?
Application security is critical because application-layer attacks—specifically SaaS and web app breaches—are the most common type of attack. Cloud-native applications frequently contain sensitive data and are accessed from multiple devices and networks, making comprehensive app security a vital component of cybersecurity strategies.
These days, applications are available from everywhere. They’re accessed by different networks connected to the internet. This wide availability, although very convenient, also increases your attack surface—and makes apps vulnerable to threats and data breaches. It’s not enough to secure the network. For applications to remain secure, protection must extend to the apps themselves.
What are application security solutions?
Authentication
Authentication refers to the process of verifying the identity of an end user before granting access to an application. When software developers create an application, they add protocols to ensure only authorized users can access it. Authentication procedures may require user login credentials like a username and password, as well as multi-factor authentication and biometrics.
Authorization
Once the authentication verification process has finished, users can then be authorized to access and use the application. This feature involves validating the user’s permission to access the application by comparing the user’s identity with a list of authorized users. Applying authentication before authorization ensures the application will only grant access after credentials have been verified.
Testing
Continuous security testing is a vital process in application development. It ensures proper security controls are in place to prevent application vulnerabilities that can be exploited.
Encryption
Making sure only authorized users access the application is not enough. Hackers and cybercriminals must be prevented from seeing or using the sensitive data in the application. Encryption does this by scrambling the data going to and from the application.
What are the different types of application security?
Application security measures can be classified according to their environment. The three primary classifications are:
Cloud application security
Cloud application security consists of the solutions, processes, and practices used to protect the sharing and exchange of data in collaborative cloud environments. Because cloud environments usually provide shared resources, it’s important to implement the principle of “least privilege.” That means making sure users access only what they’re authorized for and need to complete their tasks.
Common cloud application security processes include security testing and secure web gateways. It also involves securing the architecture. As more enterprises adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, cloud app security needs to adapt to these environments. Cloud security architecture assesses the environment for application gateways, identity verification systems, and enterprise datacenter deployments.
Web application security
While cloud application security involves securing the environment, web application security involves securing the applications themselves. Web applications are applications or services that users can access via an internet browser. Securing the applications is important for organizations that provide web services or host applications in the cloud because they must protect them from cybercriminal intrusions.
An example of web application security is the web application firewall. This solution acts as a filter, inspecting incoming data packets and blocking suspicious traffic.
Mobile application security
Most applications are used on mobile devices. Because mobile devices transmit and receive information over the public internet, they’re vulnerable to attack. Organizations often use virtual private networks, access control, and other security measures to prevent unauthorized access to data. Encryption is another common method employed to provide an extra layer of security for mobile data.
What are some application security best practices?
Securing applications and their environments can be a challenge. Fortunately, applying best practices can improve an organization’s application security posture. A good framework to follow includes four steps:
- Evaluate application security. The first step is to understand the security status of your applications by evaluating your application security. This procedure audits what applications you have, who uses them, and when. The evaluation should also include any compliance requirements or regulatory mandates you need to follow for each application
- Conduct an application security assessment. Next, it’s important to identify which applications you need to secure, which ones to test, and the security status of each one. Regulations like GDPR, PCI, and HIPAA each have unique requirements to ensure the security of private information contained in applications. The assessment provides a clear understanding of any improvements you need to make to meet compliance.
- Test your application security. After getting a clear picture of the status of your application security, the next step is to conduct security tests on your on-premises and cloud applications. Both the applications and its environment must be assessed to detect any potential security risks or vulnerabilities. Using third-party security testing tools can help prevent blind spots or biases
- Fix vulnerabilities with application security solutions. Once testing reveals any potential issues and vulnerabilities in your applications, the next step is to fix them as quickly as possible. To achieve that, you should have a security program in place that enables you to address vulnerabilities as soon as they’re discovered. By doing so, you can prevent zero-day attacks.
Common measures to address vulnerabilities include making sure all software updates are done in a timely manner. Doing updates on schedule (as opposed to ad hoc) will ensure every user gets the latest security patches at the same time. Companies should also make sure their vendors are aware of patches so they can apply them.
How is application security applied at the development level?
For developers, application security starts by using secure code and secure development processes. Implementing DevSecOps (development, security, and operations) practices involves baking security controls in early and throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC). Common procedures include automatically carrying out security testing on every piece of code before delivering it into production.
Developers should also be aware of potential threats and vulnerabilities, such as the ones provided by Open Web Application Security Project in the OWASP Top 10—a regularly-updated list of the most critical application security threats.
It is not enough, however, to identify security flaws during application development. DevOps professionals and IT security teams need to protect the entire application development process against common threat methods including phishing, malware, and SQL injection attacks.
How is application security applied at the IT level?
At the enterprise level, several application security solutions and automation strategies are available to secure applications. For instance, secure application delivery simplifies the process of applying consistent security policies across multi-cloud environments.
Another solution is to implement a web application firewall. This solution filters incoming traffic to applications to detect potential threats and intrusions. Next-generation web application firewalls employ artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities to monitor app behavior and user interactions. These advanced technologies enable organizations to mitigate both known and unknown attacks. They usually provide recommendations for remediation and help complying with regulatory standards.
Securing access to digital workspaces is vital in enterprise environments. Since cloud applications can be accessed from anywhere and from any device, organizations need to ensure access security that doesn’t disrupt the employees’ experience. Implementing access control policies and a zero trust security approach may help achieve security without compromising the ease of use.
NetScaler application security
NetScaler application security provides a comprehensive approach to protecting your applications and APIs and ensuring a consistent security posture across multi-cloud environments.
Get started with NetScaler
Request a demo or talk to sales
1-866-NetScaler